Application of Thermal Imaging Technology in Safe Driving
Share
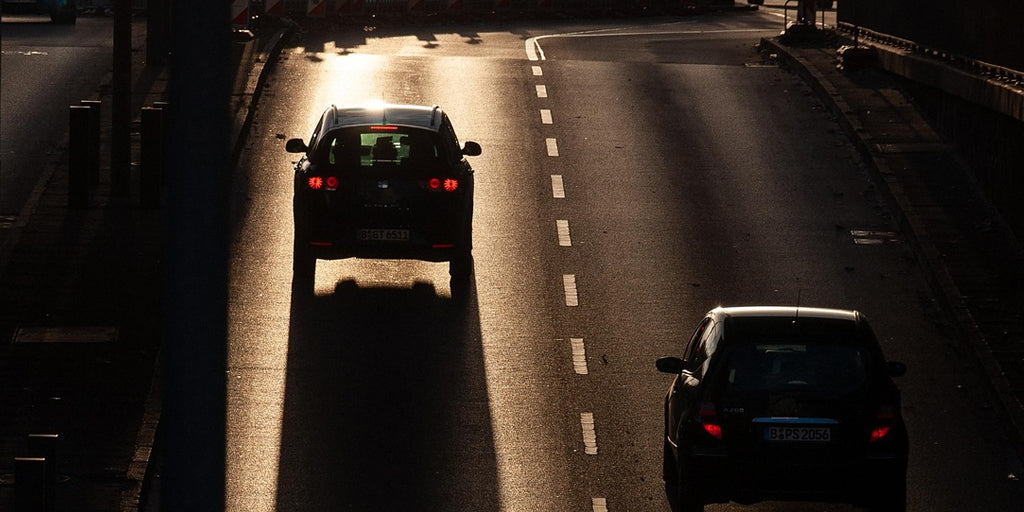
In today’s fast-evolving automotive landscape, safety features have transcended traditional seat belts, airbags, and anti-lock braking systems. Emerging technologies, such as thermal imaging, are redefining how drivers perceive and interact with their environment. Thermal imaging technology—once limited to military and industrial applications—has found a pivotal role in enhancing road safety for everyday drivers. By detecting heat signatures rather than relying on visible light, thermal imaging provides drivers with a unique perspective of their surroundings, particularly in low-visibility conditions. This article explores the applications of thermal imaging technology in safe driving, its benefits, real-world use cases, and future trends that promise to further revolutionize road safety.
1. Introduction to Thermal Imaging Technology
Thermal imaging cameras capture infrared radiation, which all objects emit as a function of their temperature. Unlike conventional cameras that depend on visible light, thermal imagers convert heat into a visible image, displaying temperature differences as varying shades or colors. Warmer objects typically appear brighter or in warmer hues (like red or orange), while cooler objects appear darker. This capability allows thermal cameras to “see” in total darkness, fog, smoke, or adverse weather conditions, making them invaluable for enhancing driving safety in scenarios where traditional lighting systems fail.
2. How Thermal Imaging Enhances Driving Safety
2.1 Improved Visibility in Low-Light Conditions
Night driving poses significant challenges as headlights illuminate only a limited area, often leaving drivers unaware of obstacles beyond the beam’s reach. Thermal imaging fills this gap by detecting the heat signatures of pedestrians, animals, or obstacles even in pitch-black environments. This enhanced visibility can be especially critical on rural roads or poorly lit urban streets where traditional lighting is inadequate.
- Early Hazard Detection: Thermal cameras can detect pedestrians, animals, or other vehicles from a greater distance, giving drivers more time to react.
- Reduced Glare Issues: Unlike headlights that can cause glare and temporary blindness, thermal imaging provides clear, distraction-free views of the surroundings.
2.2 Enhanced Performance in Inclement Weather
Adverse weather conditions—such as fog, rain, or snow—significantly reduce the effectiveness of conventional vehicle lighting. Thermal imaging systems are less affected by these conditions because they rely on temperature differences rather than light.
- Fog and Rain Penetration: In foggy or rainy conditions, thermal imagers can highlight the heat emitted by vehicles and living beings, making them visible even when traditional cameras struggle.
- Improved Navigation: Drivers can maintain a better awareness of the road and potential hazards, which helps prevent accidents during adverse weather.
2.3 Early Detection of Road Hazards
Thermal imaging isn’t just about seeing in the dark—it also aids in detecting hazards that might not be visible to the naked eye during daylight.
- Obstacles and Debris: Thermal cameras can detect temperature differences that indicate the presence of road debris, oil spills, or other hazards that might be overlooked in standard imaging.
- Mechanical Failures: Overheating components, such as brakes or engines, emit distinct heat signatures. Detecting these early can prompt preventative maintenance, potentially avoiding dangerous situations on the road.
- Animal Detection: In rural or suburban areas, animals can unexpectedly cross the road. Thermal imaging allows drivers to spot them in advance, reducing collision risks.
2.4 Complementing Other Safety Technologies
Thermal imaging technology is rapidly being integrated with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), creating a multi-layered safety net that enhances overall vehicle safety.
- Collision Avoidance: Combined with radar and lidar, thermal imaging contributes to collision avoidance systems by offering an additional layer of data. This fusion of sensor inputs improves object detection and classification, especially under challenging conditions.
- Enhanced Night Vision: When integrated with head-up displays (HUDs) or infotainment systems, thermal imaging provides drivers with a real-time overlay of potential hazards, enabling more informed and safer driving decisions.
- Autonomous Driving: For self-driving vehicles, thermal imaging is becoming a key component in the sensor suite, ensuring that autonomous systems can detect and react to obstacles, pedestrians, and other heat-emitting objects, even in low-visibility environments.
3. Real-World Applications of Thermal Imaging in Safe Driving
3.1 Urban Night Driving
Urban environments, with their mix of streetlights, shadows, and unexpected pedestrian movements, present unique challenges at night. Thermal imaging systems can assist drivers by:
- Detecting Pedestrians: Even when pedestrians are partially hidden by shadows or street furniture, thermal cameras pick up their heat signatures, alerting drivers to potential hazards.
- Identifying Road Hazards: Objects like bicycles, scooters, or even animals can be detected early, preventing collisions and enhancing overall road safety.
- Reducing Driver Fatigue: By providing clear, unambiguous images of the surroundings, thermal imaging reduces the strain on drivers, helping them remain alert and focused.
3.2 Off-Road and Rural Driving
In off-road and rural settings, where streetlights are sparse and obstacles can appear unexpectedly, thermal imaging offers significant advantages:
- Enhanced Navigation: Off-road drivers benefit from the ability to see through dark, unlit trails. Thermal imaging can reveal hidden obstacles such as rocks, logs, or uneven terrain.
- Wildlife Detection: In rural areas, animals crossing the road may not be easily visible. Thermal imaging helps drivers detect these potential hazards early, reducing the likelihood of collisions.
- Improved Situational Awareness: The technology enables a broader view of the environment, allowing drivers to identify potential hazards well in advance and adjust their driving accordingly.
3.3 Commercial Fleet and Security Applications
For commercial fleet operators and security-sensitive vehicles, thermal imaging provides additional safety and operational benefits:
- Fleet Safety: Companies can equip their vehicles with thermal imaging systems to ensure driver safety during night-time or adverse weather conditions. Enhanced visibility helps reduce accidents and improves overall fleet efficiency.
- Security and Surveillance: Vehicles used in security or law enforcement benefit from thermal imaging by detecting unauthorized individuals or potential threats in dark or concealed areas.
- Remote Monitoring: Integrated with telematics systems, thermal imaging allows fleet managers to monitor the environment around vehicles in real time, providing an additional layer of security and operational oversight.
4. Future Trends in Thermal Imaging for Safe Driving
As technology advances, thermal imaging is set to become an even more integral part of automotive safety systems. Here are some key trends shaping the future of thermal imaging in safe driving:
4.1 Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Enhanced Object Recognition: AI algorithms are improving the ability of thermal imaging systems to distinguish between different types of objects. For instance, future systems may differentiate between a pedestrian and an animal, prioritizing alerts based on the level of risk.
- Predictive Safety: AI-powered analysis of thermal imaging data could predict potential hazards before they fully materialize, allowing for proactive safety measures.
4.2 Improved Connectivity and IoT Integration
- Seamless Data Sharing: Enhanced connectivity will allow thermal imaging systems to share data with other vehicle systems and cloud-based platforms, creating a more comprehensive picture of the vehicle’s surroundings.
- Centralized Fleet Management: For commercial vehicles, IoT integration will enable real-time monitoring of thermal imaging data across entire fleets, leading to better risk management and operational efficiency.
4.3 Advancements in Sensor Technology
- Higher Resolution and Sensitivity: Ongoing improvements in sensor technology will result in thermal imagers with higher resolution and greater sensitivity, providing more detailed images and more accurate detection of heat signatures.
- Miniaturization: As components become smaller and more energy-efficient, thermal imaging systems will become more compact, making them easier to integrate into a wider range of vehicles without compromising performance.
4.4 Integration with Augmented Reality (AR)
- Real-Time Overlay: Future vehicles may integrate thermal imaging with augmented reality displays, allowing drivers to see a real-time overlay of thermal data on their windshield. This can enhance situational awareness without distracting the driver.
- Enhanced Navigation and Safety Alerts: AR integration can provide clear, visual cues for potential hazards, such as highlighting warm objects that may pose a danger, further enhancing driver response times.
5. Implementation Considerations
For drivers and fleet operators looking to adopt thermal imaging technology, several key considerations should be taken into account:
5.1 Cost and Value
- Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Benefits: While thermal imaging systems may represent a higher initial investment compared to traditional safety features, the long-term benefits in terms of reduced accidents and enhanced safety can justify the cost.
- Return on Investment (ROI): For commercial fleets, the improved safety and efficiency provided by thermal imaging can lead to significant cost savings over time, reducing downtime and maintenance expenses.
5.2 Installation and Integration
- Compatibility: Ensure that the thermal imaging system is compatible with your vehicle’s existing technology and can be integrated seamlessly with other safety systems such as collision avoidance and lane departure warnings.
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface is crucial, especially for drivers who may not be technically inclined. The system should offer clear, actionable data without overwhelming the driver.
- Professional Installation: For optimal performance, professional installation and calibration of the thermal imaging system may be necessary to ensure that it functions accurately under all conditions.
5.3 Regulatory and Legal Considerations
- Compliance: Ensure that any thermal imaging system installed in your vehicle complies with local and national regulations. Some jurisdictions may have specific requirements regarding the use of thermal imaging technology in vehicles.
- Privacy Concerns: For systems that record or transmit data, consider the privacy implications and ensure that data handling complies with applicable privacy laws and best practices.
6. Real-World Success Stories
Case Study 1: Enhancing Night-Time Safety for Emergency Vehicles
A metropolitan fire department integrated thermal imaging cameras into their emergency vehicles. The technology allowed drivers to detect pedestrians and obstacles in low-visibility conditions, significantly reducing response times and enhancing overall safety during night-time operations.
Case Study 2: Improving Fleet Safety for a Logistics Company
A major logistics company equipped its fleet of delivery trucks with thermal imaging systems. Drivers reported increased awareness of road hazards, particularly during night deliveries in rural areas. The system’s real-time alerts helped prevent accidents, and fleet managers noted a decrease in incident-related downtime, leading to higher operational efficiency.
Case Study 3: Boosting Off-Road Safety for Adventure Vehicles
An off-road tour operator installed thermal imaging systems in its fleet of adventure vehicles. The technology proved invaluable in challenging terrains and during nighttime excursions. The ability to detect heat signatures from obstacles and wildlife allowed drivers to navigate safely, enhancing the overall customer experience and reducing the risk of accidents.
Thermal imaging technology is rapidly emerging as a game-changer in automotive safety. Its ability to detect heat signatures under low-light or adverse weather conditions provides drivers with an unprecedented level of situational awareness. From improving night-time visibility and detecting hidden hazards to integrating seamlessly with advanced safety systems, thermal imaging enhances safe driving in ways that traditional technologies cannot.
As the automotive industry continues to embrace innovative technologies like AI, IoT, and augmented reality, the role of thermal imaging is set to expand further. Drivers, fleet operators, and vehicle manufacturers alike are recognizing that this technology not only saves lives but also improves the overall driving experience.
In a world where every second counts and safety is paramount, installing a thermal imaging system in your vehicle is a proactive step towards preventing accidents, ensuring reliable navigation, and making informed decisions on the road. Whether you’re a daily commuter, a commercial fleet operator, or an off-road adventurer, embracing thermal imaging technology can transform your driving experience—making every journey safer and more secure.
Ultimately, the application of thermal imaging in safe driving is about harnessing advanced technology to see what the naked eye cannot. It’s about empowering drivers with real-time data that can make all the difference between a near miss and a collision. As we look to the future, the integration of thermal imaging with other advanced driver-assistance systems promises a new era of safety, where vehicles are not just modes of transportation but intelligent, responsive entities designed to protect their occupants. Embrace thermal imaging technology today, and drive with the confidence that comes from knowing you have an extra layer of safety built into your vehicle.
Recommended Thermal Imagers from leagend